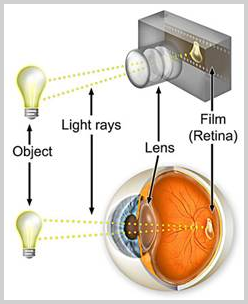
How Eye Works
HOW DOES THE EYE WORKS?

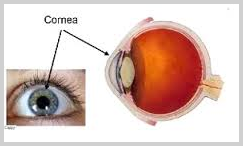
THE CORNEA
The cornea is the clear, protective outer layer of the eye. Along with the sclera (white of the eye), it serves as a barrier against dirt, germs, and other particles that can harm the eye’s delicate components. The cornea is also capable of filtering out some amounts of the sun’s ultraviolet light but enough to replace the need for wearing wraparound sunglasses outdoors.
The cornea also plays a key role in vision. As light enters the eye, it is refracted, or bent, by the outside shape of the cornea. Because there are no blood vessels in the cornea, it is normally clear and has a shiny surface. though extensive contact lens use and some corneal disease may cause blood vessels to grow over the clear cornea. The term “corneal disease” refers to a variety of conditions that affect mainly the cornea. These include infections, degenerations, and many other disorders of the cornea that may arise mostly as a result of heredity.
AQUEOUS HUMOR
AQUEOUS in the eye
Aqueous is a thin, watery fluid located in the anterior and posterior chambers of the eye. The anterior chamber lies between the iris (colored part of the eye) and the inner surface of the cornea (the front of the eye). The posterior chamber is located behind the iris and in front of the lens. In addition to supporting the shape of this area, aqueous supplies nutrients and nourishment to parts of the eye that lack blood supply. It also removes waste.
The fluid maintains an eye pressure in the range of 10 – 20 mm of Hg inside the eye, by constant circulation. If the out flow of this fluid is blocked or obstructed it leads to excessive pressure build up inside the eye and is known as Glaucoma and subsequently results in loss of vision.

THE LENS
The lens is a transparent structure behind the iris, the coloured part of the eye. The lens bends light rays so that they form a clear image at the back of the eye – on the retina. As the lens is elastic, it can change shape, getting fatter to focus close objects and thinner for distant objects.
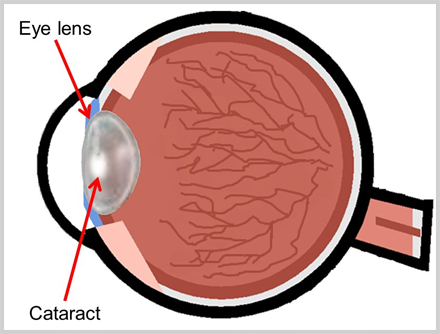
This lens under goes whitening or opacification with ageing resulting in cataract.Many other factors like use of steroids eye drops, oral medications, injuries to eye, some metabolic diseases can lead to cataract.The procedure of cataract removal (Phaco-Emulsification) is performed to correct this problem.
VITREOS HUMOR
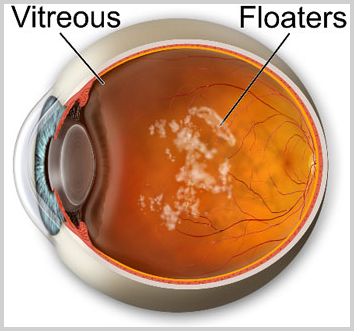
VITREOS HUMOR GEL in the eye
The vitreous humor is a jelly-like liquid that fills the cavity of the eye. It is stuck to the retina, Without the vitreous humor, your eye would seem like a collapsed ball. In old people this gel shrinks and separates from the retina and causes retinal detachment or tears in few persons. These tears cause flashes and floaters to appear in the vision.
THE RETINA
The retina is utmost sensitive and one of the most vital parts of the eye. The retina is the light-sensitive inner lining of the back of the eye. Imagine that the eye is like a non-digital camera, and the retina is the film. Rays of light enter the eye and are focused on the retina by the cornea and lens. The retina produces an image which is sent along the optic nerve for the brain to interpret, rather like developing a camera film.